The 1999 Dodge Dakota, a reliable truck known for its durability and versatility, has a fuse box that plays a crucial role in protecting its electrical system. As a car enthusiast, I’ve encountered many situations where understanding the fuse box diagram saved the day. Whether it’s a blown fuse causing a malfunctioning headlight or a faulty accessory draining your battery, knowing where to find the fuse and how to replace it is essential for any Dakota owner.

Image: schematicenginemoller.z19.web.core.windows.net
This article will provide you with a comprehensive guide to understanding the 1999 Dodge Dakota fuse box diagram. We’ll explore the different fuse box locations, identify key fuses, explain how to interpret the diagram, and offer practical tips for troubleshooting electrical issues. Get ready to empower yourself with the knowledge you need to confidently navigate the electrical system of your Dakota.
Understanding the 1999 Dodge Dakota Fuse Box Diagram
The 1999 Dodge Dakota has two main fuse boxes: the underhood fuse block and the inside fuse panel. The underhood fuse block is usually located in the engine compartment, near the battery. The inside fuse panel is typically situated on the driver’s side of the dashboard. The diagrams for these fuse boxes provide a detailed layout of all the fuses and relays, including their amperage ratings and the specific circuits they protect.
Each fuse in the diagram represents a specific electrical component or system in your Dakota. The diagram also includes information on relay locations and functions, which are essential for understanding the complex electrical network of your vehicle. When a fuse blows, it serves as a protective measure, preventing damage to the electrical system. By understanding the fuse box diagram, you can quickly identify which fuse needs to be replaced to restore power to the affected component.
Key Fuses to Know
Underhood Fuse Block
1. **Battery Fuse:** This fuse protects the battery from excessive current draw. A blown battery fuse can prevent the car from starting.
2. **Starter Fuse:** This fuse protects the starter motor. A blown starter fuse will prevent the engine from cranking.
3. **Headlamp Fuse:** This fuse protects the headlights. A blown headlamp fuse will cause the headlights to malfunction.
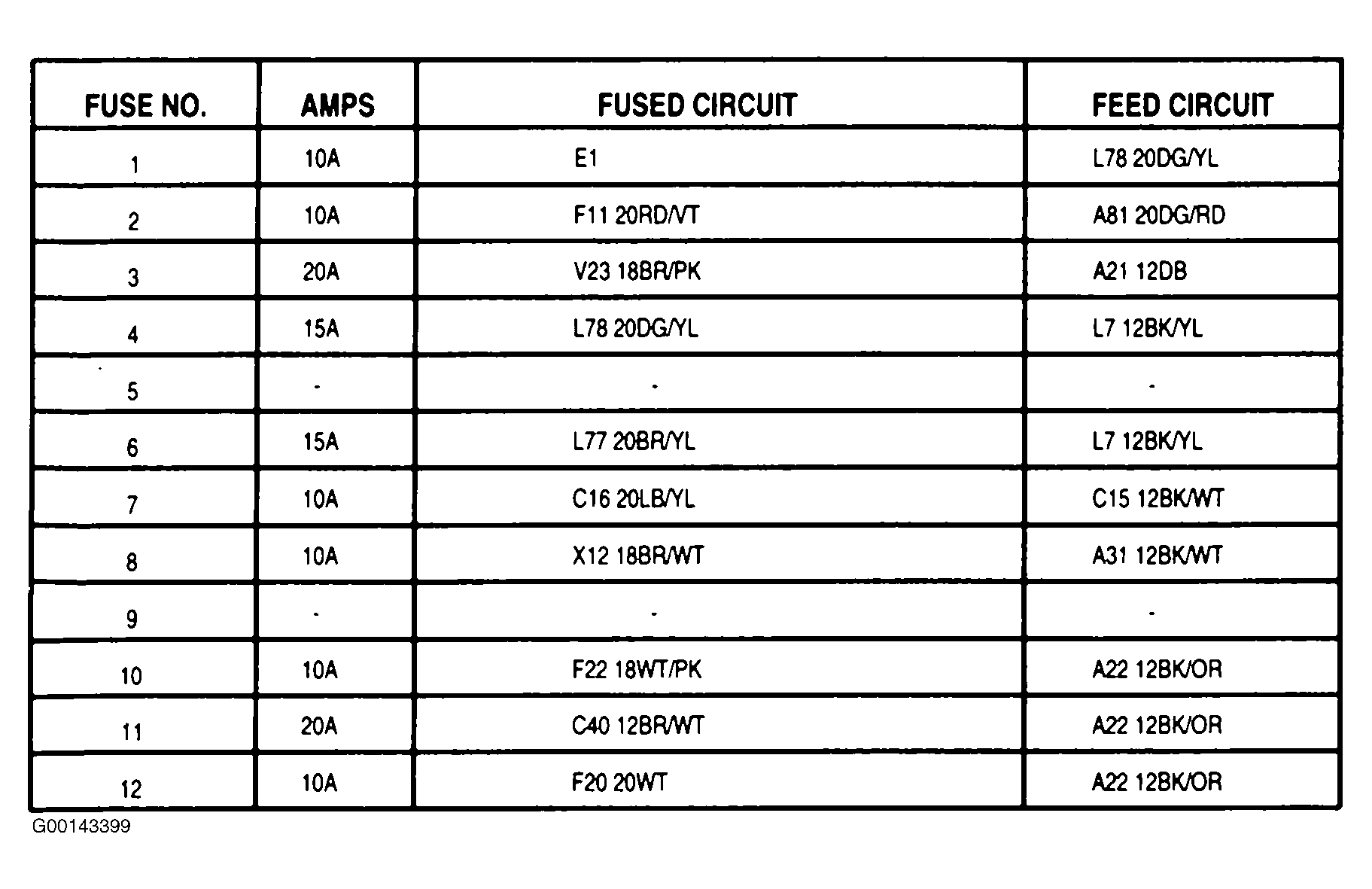
Image: guidemanualschuhmacher.z19.web.core.windows.net
Inside Fuse Panel
1. **Power Window Fuse:** This fuse protects the power window motors. A blown power window fuse will prevent the windows from rolling up or down.
2. **Radio Fuse:** This fuse protects the radio. A blown radio fuse could cause the radio to stop working.
3. **Cigarette Lighter Fuse:** This fuse protects the cigarette lighter and any accessories plugged into it. A blown cigarette lighter fuse will prevent the lighter from heating up.
Interpreting the Fuse Box Diagram
The 1999 Dodge Dakota fuse box diagram can seem intimidating at first, but it’s actually quite simple to read. The diagram usually includes the following information:
- Fuse Number: This is the number that corresponds to a specific fuse on the diagram and the physical fuse box.
- Fuse Amperage: This is the maximum amount of current that the fuse can handle before blowing.
- Circuit Description: This describes the electrical component or system that the fuse protects.
To verify if a fuse needs to be replaced, you can use a test light or multimeter. First, locate the corresponding fuse in the diagram. Next, carefully remove the fuse from the fuse box. Touch the test light probe to both ends of the fuse. If the light illuminates, the fuse is good. If the fuse is blown, it will show no continuity, and the test light will not illuminate.
Troubleshooting Tips
Here are some additional tips to help you troubleshoot your 1999 Dodge Dakota’s electrical system:
- Check the fuse diagram carefully: Make sure you are looking at the correct diagram for your year and model of Dakota.
- Inspect for loose connections: Check all the connectors and wiring in the fuse box area for any loose or damaged connections.
- Use the correct fuse amperage: Always replace blown fuses with fuses of the same amperage rating. Using a fuse with a higher amperage can damage the electrical system.
- Consider consulting a professional: If you are unable to identify and solve the electrical issue, it is always a good idea to seek the assistance of a qualified automotive technician.
FAQ
Q: Where can I find the fuse box diagram for my 1999 Dodge Dakota?
A: You can typically find the fuse box diagram in the owner’s manual for your 1999 Dodge Dakota. You can also find it online through websites like Dodge’s official website or automotive repair forums.
Q: What should I do if I can’t find the fuse box diagram?
A: If you cannot find the diagram in the owner’s manual or online, you can contact a Dodge dealership or a certified automotive mechanic. They can typically provide you with the information you need.
Q: Can I replace a blown fuse with a piece of wire?
A: Absolutely not! Replacing a fuse with a piece of wire is extremely dangerous and could cause serious damage to your Dakota’s electrical system. This practice bypasses the safety mechanism of the fuse and increases the risk of fires and other electrical hazards.
Q: What are some common signs of a blown fuse?
A: Some common signs of a blown fuse include:
- Electrical components not working (e.g. headlights, radio, power windows).
- A burnt smell coming from the fuse box area.
- A melted or broken fuse in the fuse box.
99 Dodge Dakota Fuse Box Diagram
Conclusion
Having a solid understanding of the 1999 Dodge Dakota fuse box diagram empowers you to address electrical issues confidently. While the electrical system of a vehicle can seem complex, equipped with the right information, you can easily troubleshoot simple problems. If you have any additional questions or want to learn more about the electrical system of your Dakota, feel free to leave a comment below. Are you interested in learning more about this topic? Let me know! I’m always happy to share my expertise in helping car owners be more comfortable with their vehicles.






