Have you ever wondered what makes up the intricate tapestry of life? From the tiniest bacteria to the grandest of trees, every living organism is composed of fundamental units called cells. These microscopic factories perform incredible feats, carrying out the essential functions that keep us alive. But not all cells are created equal. Just like different cells in our bodies have specialized roles – from muscle cells to nerve cells – there’s a diverse spectrum of cell types across the living world.
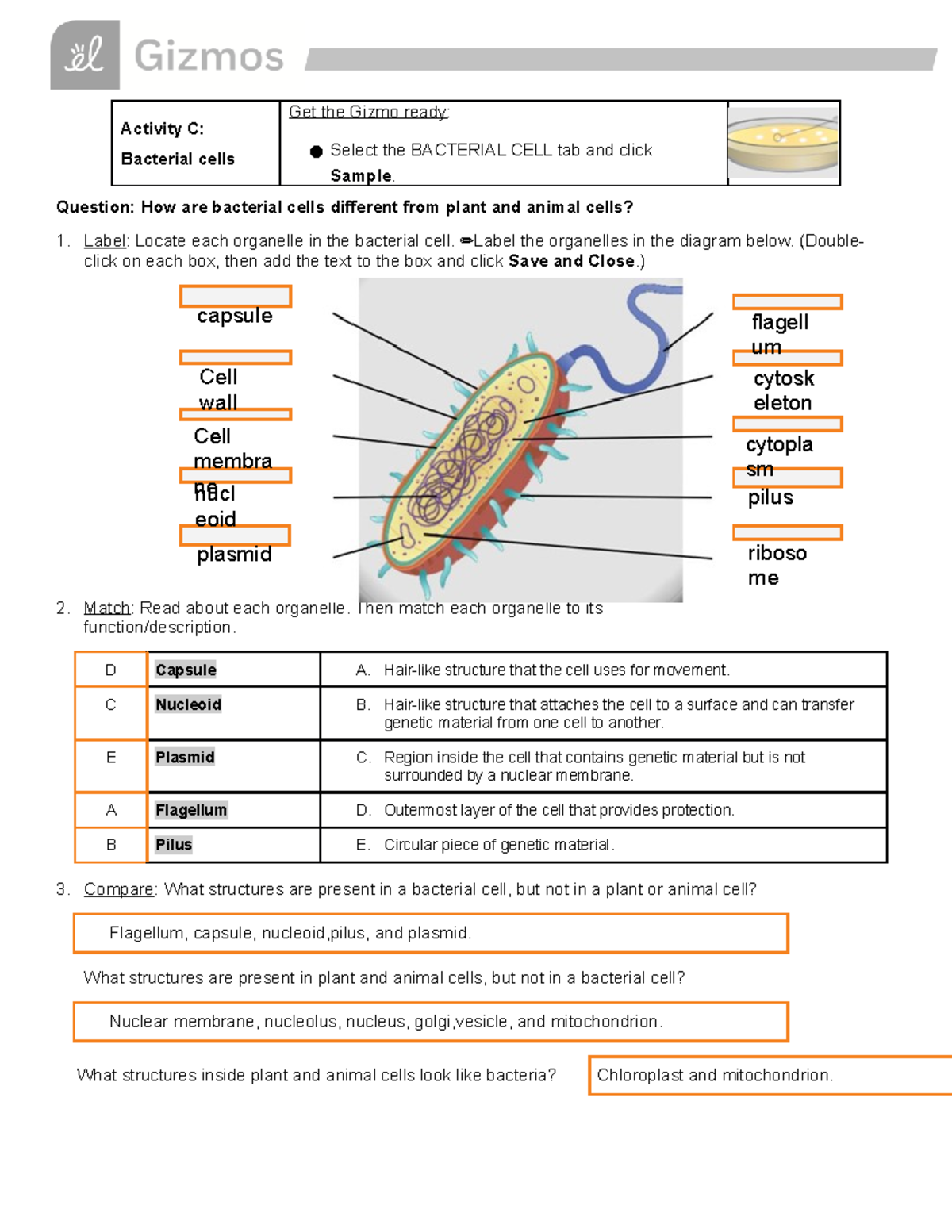
Image: www.studocu.com
The Cell Types Gizmo, a popular interactive tool for biology students, provides a fascinating journey into the world of cell structures and functions. Activity B, in particular, delves deeper into the unique characteristics of different cell types, helping students understand how their differences dictate their specialized roles. As you embark on this cellular adventure, it’s important to have the right tools and resources. This article will serve as your guide, offering a comprehensive overview of Activity B’s key concepts and providing insights into the wonders of cell diversity.
Exploring Cell Types: A Deeper Dive
Activity B in the Cell Types Gizmo takes you beyond the basic structures found in all cells and delves into the specific features that make each cell type unique. Imagine a world where you can explore the intricate details of a plant cell, from its chloroplasts, where photosynthesis takes place, to its rigid cell wall, which provides structural support. Or picture yourself peering into the complex workings of a nerve cell, with its long, thread-like extensions called axons that transmit electrical signals throughout your body.
As you navigate through this activity, you’ll encounter a range of cell types, each with a specific role to play in the bigger picture of life. From the muscle cells that power your movement to the immune cells that defend your body against invaders, every cell type contributes to keeping you alive and functioning.
Key Concepts: Understanding the Diversity
To truly grasp the essence of Activity B, it’s important to understand the key concepts that underpin the fascinating world of cell diversity. Here are some of the key concepts you’ll encounter:
1. Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells
The very first distinction you’ll encounter is between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. This fundamental difference determines the organizational complexity of an organism’s cells. Prokaryotic cells, found in bacteria and archaea, lack a true nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles, making them relatively simpler in structure. Eukaryotic cells, on the other hand, have a well-defined nucleus that houses their genetic material and a variety of organelles performing specialized functions. This distinct feature allows for greater complexity in eukaryotic organisms, including plants, animals, fungi, and protists.

Image: www.studypool.com
2. Cell Structures and Functions
Each cell type possesses a unique set of structures, called organelles, that enable it to carry out specific functions. For instance, plant cells have chloroplasts, which contain chlorophyll and are crucial for photosynthesis. Animal cells, conversely, have lysosomes, which act as the cell’s recycling centers, breaking down waste products. By understanding the relationship between an organelle’s structure and its function, you can gain a deeper insight into the intricate workings of each cell type.
3. Specialization and Differentiation
The amazing diversity of cell types arises from the process of cell differentiation, where cells with identical genomes develop specialized structures and functions. Imagine a single fertilized egg developing into a complex organism with an astounding array of cell types. This specialized division of labor allows for the efficient functioning of multicellular organisms. It’s a testament to the remarkable adaptability of life, enabling organisms to thrive in diverse environments.
4. Evolutionary Significance
The evolution of different cell types is a testament to the power of natural selection. Over billions of years, cells have adapted and evolved, developing specialized structures and functions that allow organisms to survive and thrive in diverse environments. The emergence of new cell types has been a major driver of biological diversity, allowing for the evolution of more complex organisms and the expansion of life into new habitats and ecosystems.
Current Trends and Developments: A Glimpse into the Future
Understanding cell types is not just an academic pursuit; it holds profound implications for our understanding of health and disease. Research on cell types is constantly evolving, leading to groundbreaking discoveries and innovative therapeutic approaches. For instance, stem cell research holds immense promise for regenerative medicine, allowing scientists to harness the potential of these undifferentiated cells to repair damaged tissues and organs.
Advances in single-cell sequencing technology have also revolutionized our understanding of cellular diversity. These technologies allow researchers to analyze the genetic makeup of individual cells, providing valuable insights into how cells function and how they contribute to disease development. These insights have the potential to lead to personalized medicine, where treatments are tailored to the specific characteristics of an individual’s cells.
Tips and Expert Advice: Navigating Cell Types
As you embark on your exploration of cell types in Activity B, here are some tips to enhance your understanding and make the most of this learning experience.
1. Actively Engage with the Gizmo
Don’t just passively read through the information provided; actively engage with the Gizmo by manipulating the interactive features. Zoom in on individual organelles to see their intricate details, compare and contrast different cell types, and experiment with how changing environmental conditions affect cellular processes. The more you interact with the Gizmo, the deeper your understanding of these concepts will become.
2. Relate Cell Types to Real-World Examples
To make the concepts truly relevant, relate them to real-world examples. Imagine the specialized muscle cells that allow athletes to sprint or the immune cells that fight off infections. Consider how different cell types work together to keep your body functioning properly. By applying your knowledge to real-life scenarios, you’ll solidify your understanding and appreciate the interconnectedness of life at the cellular level.
Frequently Asked Questions: Addressing Your Queries
As you delve into the world of cell types, you might have a few questions. Here are some frequently asked questions and their answers to help address your curiosities:
Q: Why are there so many different cell types?
A: The diverse range of cell types is a result of evolution and the need for specialization. Different cell types have unique structures and functions that allow multicellular organisms to perform complex tasks and thrive in diverse environments. This division of labor optimizes efficiency and allows for greater complexity in life.
Q: How are cell types different from each other?
A: Cell types differ in their structure, function, and the set of genes they express. For example, a muscle cell has elongated fibers that allow it to contract, while a nerve cell has long axons that transmit electrical signals. These differences arise from the process of cell differentiation, where cells with the same genetic code develop specialized structures and functions.
Q: Are all cells capable of becoming any cell type?
A: While all cells in an organism share the same genetic code, not all cells are capable of becoming any cell type. Some cells are highly specialized and cannot return to an undifferentiated state. However, stem cells retain the capacity to differentiate into multiple cell types, making them a promising avenue for regenerative medicine.
Cell Types Gizmo Answer Key Activity B
Conclusion: Embracing the Fascinating World of Cells
The Cell Types Gizmo, along with its engaging Activity B, offers a unique opportunity to explore the magnificent diversity of life at the cellular level. By understanding the key concepts of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, specialization, and adaptation, you gain valuable insights into the building blocks of life and their profound role in our world.
Are you ready to embark on this cellular adventure? Explore Activity B, engage with the interactive features, and discover the hidden wonders of the microscopic world. The journey of understanding cell types is an ongoing adventure, filled with constant discoveries and exciting opportunities for scientific exploration.






