Picture this: you’re staring at a steaming cup of coffee, the aroma swirling around your head. The liquid coffee slowly transforms into a wispy cloud of steam, rising towards the ceiling. This familiar process, known as boiling, is a perfect example of a phase change – a fundamental concept in science that governs the states of matter around us. But understanding these transitions, from solid ice to liquid water, can feel like navigating a scientific maze. Fear not! This guide unravels the complexities of phase changes, providing you with the essential knowledge and, more importantly, a comprehensive look at the “Phase Change Worksheet Answer Key PDF” – your ultimate tool for mastering this exciting realm of physics.

Image: www.pinterest.com
Phase changes are captivating not just for their scientific elegance but also for their impact in our daily lives. From the melting of ice cream on a hot summer day to the freezing of water in our refrigerators, these transformations are woven into the fabric of our existence. Understanding them is key to appreciating the world around us, unlocking the secrets behind phenomena like weather patterns, industrial processes, and even the very formation of planets. But delving into the world of phase changes can feel daunting, especially when encountering the complexities of enthalpy, entropy, and free energy. This is where the “Phase Change Worksheet Answer Key PDF” becomes your indispensable companion, unlocking the secrets behind these transformations.
The Building Blocks of Matter: A Journey Through States
Before we unravel the mysteries of the “Phase Change Worksheet Answer Key PDF”, let’s take a moment to understand the fundamental building blocks of matter – the states of matter. We encounter these states daily, but delving deeper reveals a fascinating world of molecular interactions and energy exchanges. The three primary states of matter are:
-
Solid: Solid matter is characterized by a rigid structure with molecules tightly packed together. Think of a block of ice, maintaining its shape due to the strong bonds holding water molecules in place. The molecules in a solid vibrate, but they stay relatively fixed in their positions.
-
Liquid: In the liquid state, molecules have greater freedom of movement compared to solids. Think of water flowing freely, adapting to the shape of its container. Liquids are more compressible than solids because their molecules have more space to move around.
-
Gas: Gases are the freest of all states, with molecules moving randomly and independent of each other. Imagine the air we breathe, a mixture of gases like nitrogen and oxygen, filling the entire volume of a room. Gases are easily compressible because the distance between molecules is significantly greater compared to solids and liquids.
These states of matter are not static; they can change from one to another under the influence of factors like temperature and pressure. It is in these transformations, known as phase changes, where the magic of nature truly unfolds.
Unveiling the Secrets of Phase Changes
Phase changes are transitions between different states of matter—think of ice melting into water or water vaporizing into steam. These transformations are not simply about physical changes in appearance; they involve intricate energy exchanges at the molecular level. To fully understand these phenomena, we need to explore the terminology, including the key concepts of enthalpy, entropy, and free energy.
-
Enthalpy: Enthalpy is a measure of the total energy of a system, including both its internal energy and the energy associated with pressure and volume. It tells us how much heat is absorbed or released during a phase change. For instance, melting ice requires energy input (positive enthalpy change), while freezing water releases heat (negative enthalpy change).
-
Entropy: Entropy quantifies the randomness or disorder within a system. During phase changes, entropy usually increases, meaning that the molecules become more disordered. For instance, a solid has a lower entropy than a liquid because the molecules are more confined.
-
Free Energy: Free energy is a thermodynamic quantity that determines the spontaneity of a process, specifically whether a process will occur naturally or require external energy input. Phase changes occur spontaneously when the free energy change is negative, meaning that the process is energetically favorable.
A Guided Tour of the “Phase Change Worksheet Answer Key PDF”
The “Phase Change Worksheet Answer Key PDF” functions as your ultimate guide to phase changes. This comprehensive document provides a detailed explanation of the key concepts discussed previously, along with numerous practice problems and their solutions. The PDF is meticulously structured to ensure a clear and engaging learning experience.
-
Introduction: The PDF begins with a concise introduction to phase changes, defining the different states of matter and outlining the key concepts like enthalpy, entropy, and free energy.
-
Types of Phase Changes: The next section delves into the different types of phase changes, including melting, freezing, sublimation, deposition, vaporization, and condensation, providing clear explanations of each process along with diagrams for visual clarity.
-
Calculating Enthalpy Change: This section focuses on the calculation of enthalpy changes during phase transitions. The PDF includes numerous practice problems to help solidify your understanding of the concepts and the formula for calculating enthalpy changes.
-
Entropy and Phase Changes: The PDF then explores the role of entropy in phase changes, explaining how the increase in entropy usually accompanies the transition from a solid to a liquid or a liquid to a gas. The worksheet includes practice problems involving entropy calculations and the relationship between enthalpy and entropy.
-
Free Energy and Phase Transitions: Finally, the PDF delves into the concept of free energy and how it dictates the spontaneity of phase changes. The worksheet provides practice problems where you can calculate free energy changes and determine whether a phase change is spontaneous or not.
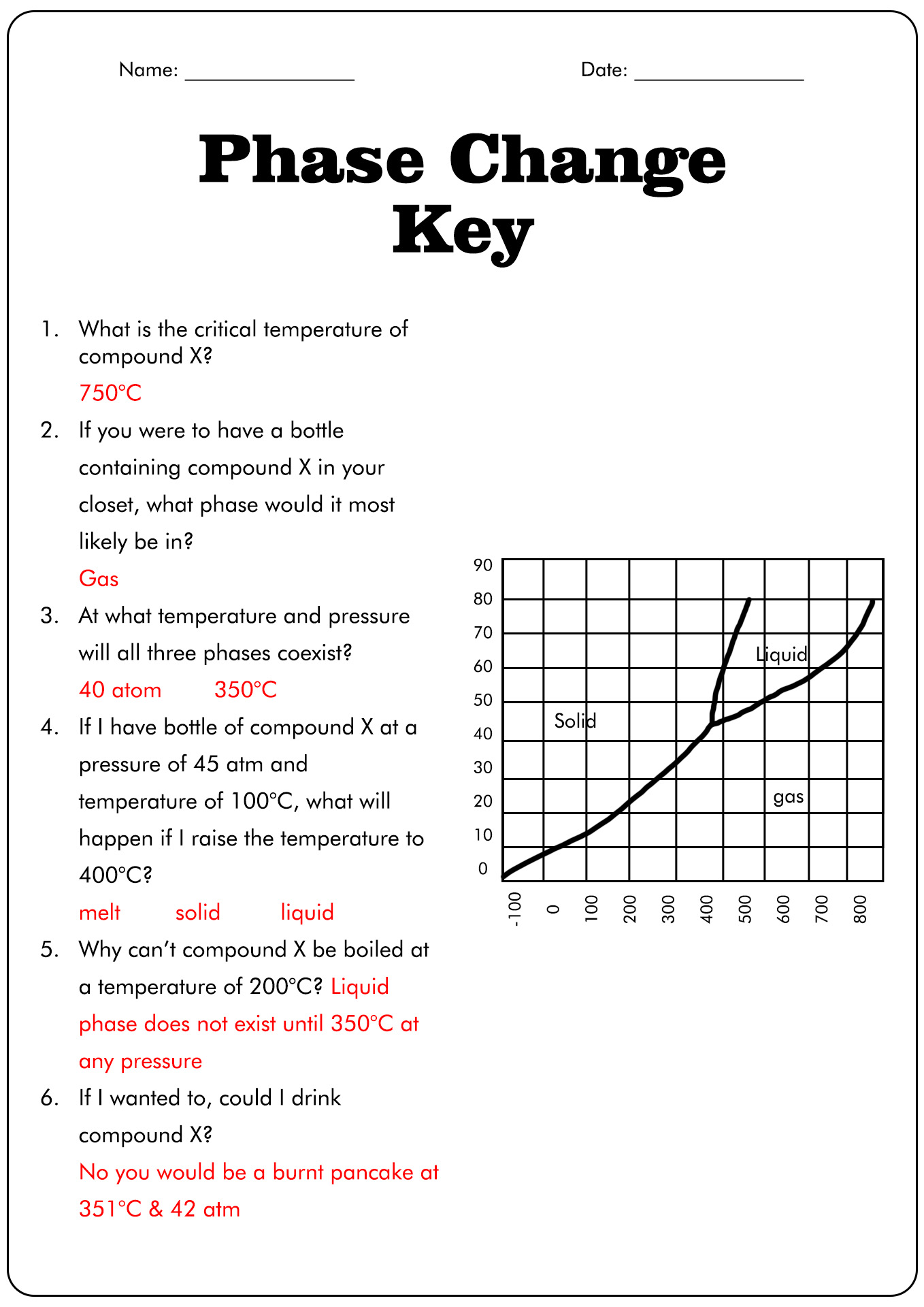
Image: materialfullstultify.z13.web.core.windows.net
Expert Insights and Actionable Tips
The “Phase Change Worksheet Answer Key PDF” is not just a tool for learning concepts; it’s a springboard for deeper understanding and application. Here’s how to get the most out of this invaluable resource:
-
Focus on Conceptual Understanding: The key to mastering phase changes lies in understanding the underlying concepts, not just memorizing formulas. The PDF provides a clear framework for understanding the relationships between enthalpy, entropy, and free energy.
-
Practice Makes Perfect: The abundance of practice problems within the PDF is crucial for building your confidence and solidifying your understanding. Don’t hesitate to work through each problem and refer to the answer key for clarification.
-
Visualize the Processes: Don’t just read the text; visualize the processes of phase changes. Imagine the molecules moving and interacting during transitions, and this will help you relate the theoretical concepts to real-world phenomena.
Phase Change Worksheet Answer Key Pdf
Conclusion
The “Phase Change Worksheet Answer Key PDF,” a powerful tool for both learning and practice, unlocks the secrets of phase changes. It provides a clear, engaging, and comprehensive guide to the intricate world of transitions between states of matter. So, whether you’re a student grappling with thermodynamics or a curious individual eager to understand the world around you, this PDF will serve as your reliable companion on your journey to mastering phase changes.
Don’t just stop at understanding; delve deeper, explore the various applications of these concepts, and revel in the fascinating world of physics that governs the changing states of matter. From understanding the intricacies of weather patterns to appreciating the processes involved in everyday phenomena like cooking and freezing, the knowledge you gain from this PDF will enhance your understanding of the world around you.






