Remember those days in high school chemistry, where the periodic table seemed like a foreign language? I certainly did. The concept of relative masses and moles was particularly confusing. Why did we care about atomic mass units? What was the big deal with this “mole” thing? It was only later, when I began to grasp the meaning behind these fundamental concepts, that chemistry started to make sense. Today, I’m going to break down those mysteries for you, demystifying them and giving you a strong foundation in the fundamentals of chemistry.

Image: alekohovekamp.blogspot.com
If you’re looking to master the world of molecules and reactions, understanding the relationship between relative mass and the mole is your key. This guide, complete with helpful examples, will turn those intimidating equations and symbols into your best friends.
Understanding Relative Mass
What is Relative Mass?
Imagine you have a bag of marbles. Each marble has a different weight, right? Relative mass works similarly in the world of atoms and molecules. We assign a number to each element, called its relative atomic mass, based on how heavy it is compared to a standard – the carbon-12 atom. This number represents the average mass of that element’s atoms, taking into account the different isotopes that occur naturally. For instance, hydrogen has a relative atomic mass of about 1, meaning it’s about 1/12th as heavy as a carbon-12 atom. Oxygen, with a relative atomic mass of about 16, is 16 times heavier than hydrogen.
How is Relative Mass Calculated?
Calculating relative mass involves comparing an atom’s mass to the mass of a carbon-12 atom. The result is a value that is relative to the mass of carbon-12. This relative atomic mass is often simply called the atomic weight and is displayed on the periodic table. The relative atomic mass is usually a decimal number, reflecting the fact that elements exist as a mixture of isotopes with different masses. We can also use the concept of relative mass to calculate the relative molecular mass of a molecule – basically, the sum of the relative atomic masses of all the atoms in that molecule.
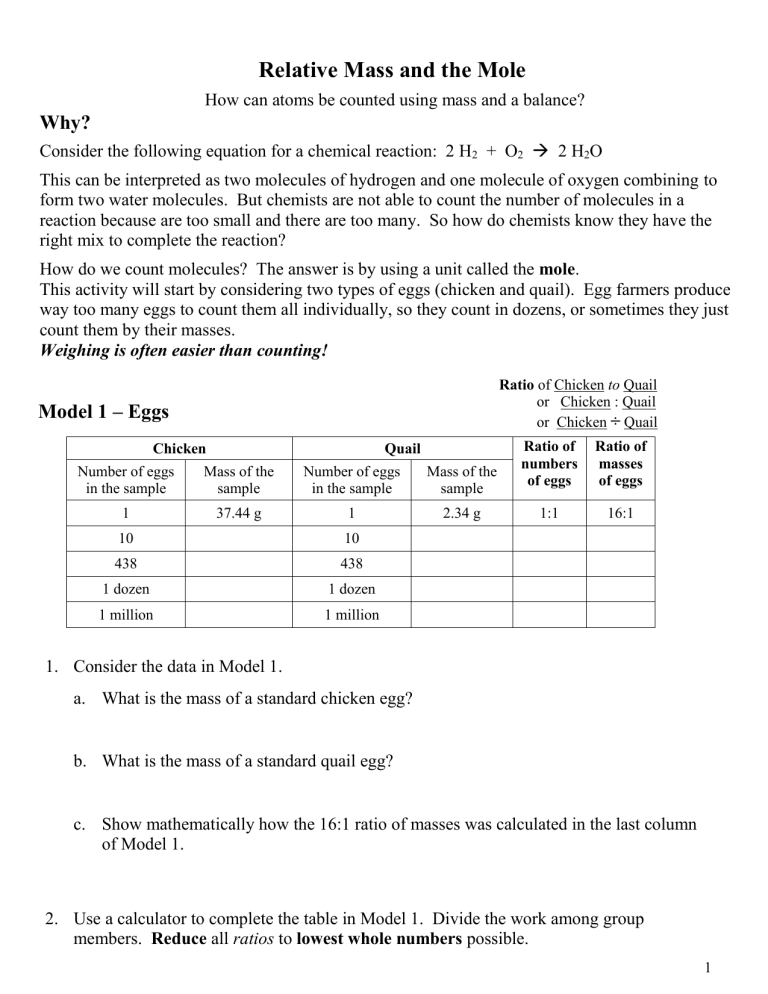
Image: gustavogargiulo.com
Diving into the Mole
Defining the Mole
The mole is a fundamental unit in chemistry that acts as a bridge between the microscopic world of atoms and molecules and the macroscopic world of masses we can measure. Think of it like a chemist’s dozen: a mole is a specific amount of a substance, just like a dozen is a specific amount of eggs. One mole of a substance contains 6.022 x 10^23 particles (atoms, molecules, or ions). This enormous number is known as Avogadro’s constant.
A Practical Perspective on Moles
Think of the mole as a convenient way to handle large amounts of atoms and molecules. Imagine you had a bag of marbles – say, 6.022 x 10^23 marbles. This bag would be incredibly large and heavy, yet it’s only one mole of marbles. Each mole has a specific mass, determined by the element or compound it represents. This consistent relationship between moles and mass is what makes the mole such a powerful tool in chemistry.
The Mole and Its Importance in Calculations
The mole plays a crucial role in chemical calculations, allowing us to relate the amount of a substance in grams to the number of particles present. For example, the molar mass of water (H2O) is 18 g/mol. This means one mole of water weighs 18 grams, and contains 6.022 x 10^23 water molecules. This connection between mass, moles, and particle number is fundamental to understanding chemical reactions and stoichiometry.
Connecting Relative Mass and Moles: A Key Equation
The concept of relative mass and the mole are interconnected through the idea of molar mass. Molar mass is simply the mass of one mole of a substance, measured in grams per mole (g/mol). It is calculated by adding up the relative atomic masses of all the atoms in a molecule. This means that if you know the relative mass of an atom, you can easily find the molar mass of any compound it forms!
Tips and Expert Advice
Here are some tips for mastering the concept of relative mass and the mole:
- Practice makes perfect: The best way to solidify your understanding is to practice calculations involving relative mass, molar mass, and the mole. Start with simple examples and gradually work your way up to more complex ones.
- Utilize the periodic table: The periodic table is your best friend! Use it to look up the relative atomic masses of different elements and calculate molar masses.
- Think in terms of particles: Always try to visualize the microscopic world of atoms and molecules when working with relative mass and moles. Remember that one mole represents Avogadro’s number of particles, and this understanding will help you grasp the true meaning of these concepts.
- Don’t be afraid to ask for help: If you’re stuck, don’t hesitate to ask your teacher, tutor, or classmates for help. There are many online resources available as well, such as videos, tutorials, and practice problems.
Remember, chemistry isn’t about memorizing equations; it’s about understanding the underlying principles. Once you have a solid understanding of relative mass and the mole, you’ll be well on your way to mastering the fascinating world of chemistry.
General FAQs
Q: Why do we need the mole concept?
A: The mole is essential for quantifying the amounts of chemicals involved in reactions. It provides a standard unit for measuring the number of particles, making it easier to compare and calculate the quantities involved in chemical reactions.
Q: What is the difference between relative atomic mass and molar mass?
A: Relative atomic mass is a dimensionless quantity representing the average mass of an atom of an element. Molar mass, on the other hand, is the mass of one mole of a substance and is expressed in grams per mole (g/mol).
Q: How can I convert between mass and moles?
A: To convert between mass and moles, you can use the equation:
**Number of moles (n) = Mass (m) / Molar mass (M)**
This equation allows you to calculate the number of moles if you know the mass and molar mass, or vice versa.
Q: Are there resources for further learning about relative mass and the mole?
A: Yes, there are numerous resources available. Online platforms like Khan Academy offer interactive lessons and practice problems. Your textbook is also a valuable source, as well as your teacher or tutor.
Relative Mass And The Mole Answer Key
https://youtube.com/watch?v=uQ6Hd2yaKVY
Conclusion
The concepts of relative mass and the mole are fundamental building blocks in chemistry. By mastering them, you open the door to an entire world of chemical reactions, calculations, and the fascinating study of matter. It’s not always an easy journey, but armed with the right tools and dedication, you can conquer it! Do you find this topic fascinating? Let’s continue the exploration together in the comments below!






