Imagine this: you’re cruising down the highway, enjoying the open road, when suddenly, your car’s headlights go out. Darkness descends, and you’re left stranded, unsure what to do. This is a scenario that could easily become a nightmare without the knowledge of your vehicle’s fuse box. Understanding the ins and outs of this critical component could be the key to getting you back on the road in a pinch.
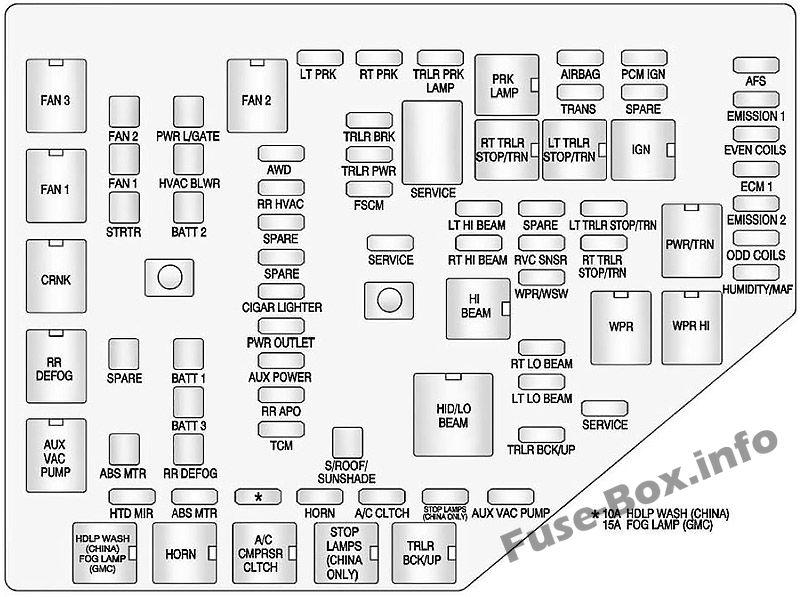
Image: aylwinsuranne.blogspot.com
The fuse box is the unsung hero of your 2008 GMC Acadia, silently guarding its electrical system from overloads and malfunctions. It’s a miniature electrical command center, housing fuses and relays that control the flow of power to your car’s various components. But understanding this intricate network can be daunting, especially for a novice. This guide will be your compass to navigate the complexity of the 2008 GMC Acadia’s fuse box, empowering you with the knowledge to tackle electrical issues with confidence.
Location, Location, Location: Finding the Fuse Box
The first step in our journey is finding the elusive fuse box. Your 2008 GMC Acadia has two key fuse box locations:
1. Under the Hood:
- Lift the hood of your Acadia and search for a black plastic box typically on the driver’s side, near the front of the engine compartment. This box houses the majority of your vehicle’s fuses, safeguarding the essential functions like headlights, engine, and power accessories.
2. Inside the Cabin:
- Locate the fuse box inside the passenger compartment, usually on the driver’s side, under the dashboard. This smaller fuse box controls the interior components like the radio, power windows, and climate control.
Decoding the Fuse Box Diagram: Your Electrical Roadmap
Once you’ve found the fuse box, the next step is to decipher the mysterious symbols and numbers that adorn the fuse box cover. This is where the trusty fuse box diagram comes into play. This diagram acts as your electrical roadmap, guiding you to the specific fuse responsible for each component in your car.
Understanding the Diagram:
- Fuse Numbers: Each fuse is labeled with a unique number. This number will be your key to locating the corresponding fuse in the diagram.
- Circuit Descriptions: The diagram will list each fuse’s corresponding circuit, indicating which system or component it controls (e.g., headlights, power windows, radio).
- Fuse Amperage: The diagram will also indicate the fuse’s amperage (the maximum current it can safely handle). This crucial information helps you select the correct replacement fuse.
Using the Diagram:
- Identify the Component: Determine which component is experiencing an electrical issue (e.g., your headlights aren’t working).
- Find the Corresponding Fuse: Refer to the diagram and locate the fuse number associated with the malfunctioning component.
- Locate the Fuse: Use the fuse number to pinpoint the physical fuse in your vehicle’s fuse box.
- Inspect the Fuse: Remove the fuse and examine it for any signs of damage or blown fuses.
- Replace If Needed: If the fuse is blown (melted or broken), replace it with a new fuse of the same amperage.
Common Fuse Problems and Solutions
Now that we’ve deciphered the fundamentals of your fuse box, let’s dive into some common fuse problems and how to solve them:
1. Blown Fuse: The most common issue is a blown fuse caused by an overload or short circuit. A blown fuse will exhibit a melted or broken filament.
Solution: Replace the blown fuse with a new fuse of the same amperage. Before replacing, troubleshoot the underlying cause of the blown fuse (e.g., a short circuit or malfunctioning component).
2. Loose Fuse: If a fuse is loose in the fuse holder, it may result in an intermittent electrical problem.
Solution: Carefully tighten the fuse in its holder. Ensure the contact points are clean and free of corrosion.
3. Corroded Fuse Holder: Corrosion in the fuse holder can disrupt electrical flow, leading to intermittent problems.
Solution: Clean the fuse holder and its contact points with a wire brush or a contact cleaner. Replace the fuse holder if it’s severely corroded.
4. Incorrect Fuse Amperage: Using a fuse with an inappropriate amperage can lead to electrical problems or even damage to your car’s electrical system.
Solution: Always use fuses with the correct amperage. Refer to your fuse box diagram to determine the correct amperage for each fuse.
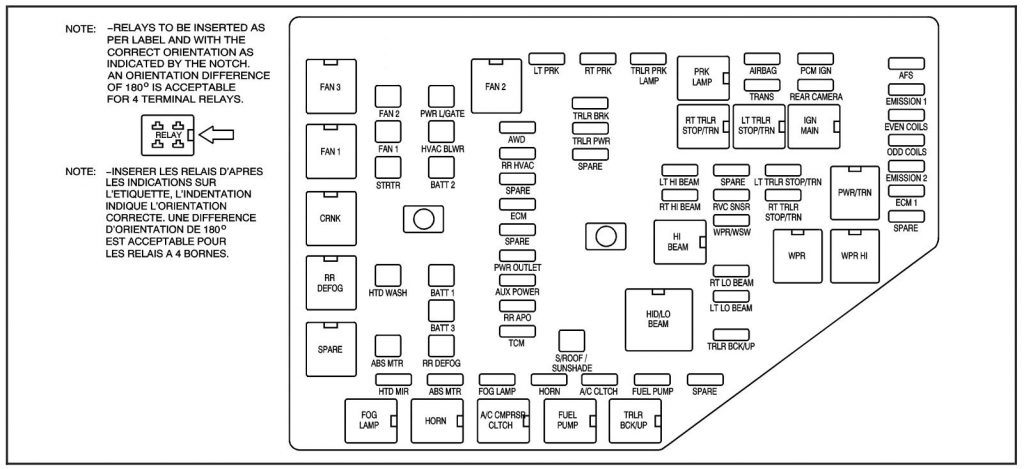
Image: www.autogenius.info
Beyond the Basics: Expanding Your Knowledge
While we’ve covered the essentials of understanding your 2008 GMC Acadia’s fuse box, there’s always more to learn.
1. Preventive Maintenance: Regularly inspect your fuse box and fuses for any signs of damage or wear. This simple practice can prevent unexpected electrical problems.
2. Consult Your Owner’s Manual: Your 2008 GMC Acadia’s owner’s manual is a valuable resource that provides specific information about your vehicle’s fuse box, diagram, and recommended fuse amperages.
3. Seek Professional Help: If you’re unsure about troubleshooting electrical issues or replacing fuses, don’t hesitate to consult a qualified mechanic.
2008 Gmc Acadia Fuse Box Diagram
Empowering You with Electrical Knowledge
By mastering the intricacies of your 2008 GMC Acadia’s fuse box, you’re not only equipped to handle minor electrical fixes but also understand the fundamental workings of your car’s electrical system. Remember, prevention is key. Regularly inspect your fuses and fuse box to ensure the smooth operation of your Acadia. Now, go forth and conquer the electrical world of your 2008 GMC Acadia with confidence!






