Imagine a burning sensation in your stomach, a gnawing pain that intensifies after meals. This is the reality for millions who grapple with peptic ulcer disease. It’s a condition that can significantly impact your quality of life, hindering your ability to enjoy meals, focus on work, or simply find comfort. But understanding the roots of this ailment and the nuances of treating it can empower you to take control and find relief.
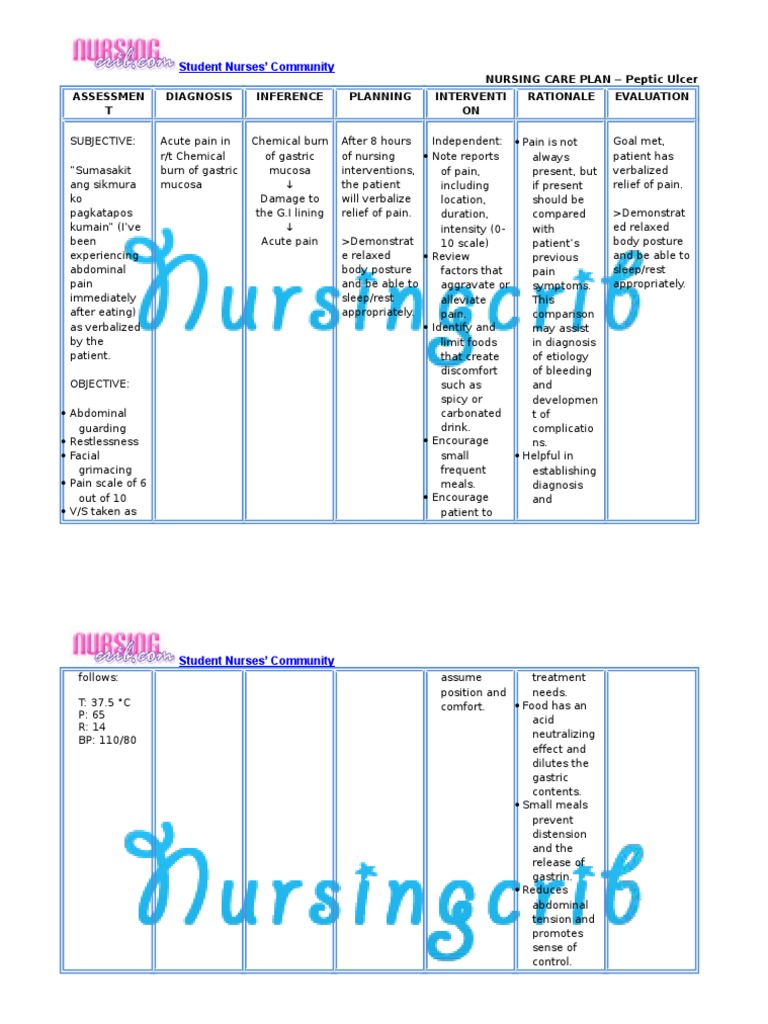
Image: es.scribd.com
This article will delve into the world of nursing diagnosis for peptic ulcer disease. We’ll explore the complexities of this condition, navigating the intricacies of its causes, symptoms, and the role of nursing in helping patients manage their condition. Join us as we uncover the crucial role nurses play in supporting those living with peptic ulcers, promoting healing, and empowering them to live healthier, happier lives.
Decoding Peptic Ulcer Disease: A Deeper Dive
Peptic ulcer disease (PUD) is a chronic condition marked by sores or ulcers that develop in the lining of the stomach or duodenum, the first part of the small intestine. These ulcers, often painful, can cause a range of uncomfortable symptoms like heartburn, nausea, and indigestion.
Common Causes: Understanding the Triggers
Several factors can contribute to the development of peptic ulcers, with the most prominent being:
- Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection: This bacteria is the most common cause of peptic ulcers. H. pylori weakens the stomach’s protective lining, making it susceptible to damage by acid.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): Commonly used medications like ibuprofen and naproxen can irritate the stomach and disrupt its natural protection.
- Excessive acid production: In some cases, the stomach may produce more acid than normal, increasing the risk of ulcer formation.
- Stress: While not a direct cause, chronic stress can trigger the release of hormones that contribute to the development of peptic ulcers.
Recognizing the Signals: Symptoms of Peptic Ulcer Disease
Peptic ulcer disease can manifest in a variety of ways. However, some common symptoms include:
- Burning pain in the stomach: This pain often occurs between meals or at night and can be relieved by eating or taking antacids.
- Nausea and vomiting: Especially after meals, these symptoms can accompany the burning pain.
- Indigestion and bloating: These discomforting sensations may occur alongside a feeling of fullness.
- Weight loss: A significant decrease in appetite can lead to weight loss, a potential indicator of a peptic ulcer.
- Black or tarry stools: This could indicate bleeding from the ulcer.
- Vomiting blood: Bright red vomit or blood in the stool are indications that the ulcer is bleeding.

Image: www.theherbaltreatment.com
The Nurse’s Role: Delivering Compassionate Care
Nurses play a pivotal role in managing peptic ulcer disease. Their expertise is crucial in assessing patients, providing education, and implementing treatment plans to help patients find relief.
Assessment: Gathering Vital Information
The nursing assessment process is essential for determining the patient’s individual needs. Nurses will:
- Obtain a comprehensive health history: This includes information about the patient’s symptoms, past medical conditions, medication history, lifestyle habits, and family history.
- Perform a physical examination: This includes assessing vital signs, examining the abdomen, and checking for any signs of bleeding or other complications.
- Review laboratory results: Nurses will analyze results of blood tests, stool tests, and endoscopic procedures to confirm the diagnosis and assess the severity of the ulcer.
Diagnosis: Understanding the Nursing Process
The nursing diagnosis for peptic ulcer disease is a complex process involving a multi-step approach:
- Analyze patient data: Using the information gathered during assessment, nurses identify problem areas and determine the patient’s needs.
- Formulate a nursing diagnosis: This involves stating the patient’s health problem, its related factors, and the characteristics of the problem. For instance, a nursing diagnosis might be “Acute pain related to gastric ulceration as evidenced by verbal reports of burning pain and use of antacids.”
- Develop nursing interventions: The nurse will create a plan of action to address the identified problem, including medication administration, pain management, and patient education.
- Implement interventions: Nurses carry out the plan, providing medications, monitoring vital signs, and offering emotional support.
- Evaluate outcomes: Nurses continually assess the patient’s progress, evaluating the effectiveness of interventions and adjusting the care plan as needed.
Interventions: Promoting Healing and Pain Relief
Nursing interventions play a vital role in alleviating symptoms and facilitating healing. Common nursing interventions include:
- Administer medications: Nurses administer medications prescribed by physicians, such as antacids to reduce stomach acid, antibiotics to eradicate H. pylori, and proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) to suppress acid production.
- Pain management: Nurses assess pain levels, provide comfort measures, and administer pain medications as ordered.
- Nutrition counseling: Nurses guide patients on appropriate dietary changes, advising them to consume smaller, more frequent meals, avoid spicy foods, reduce caffeine intake, and limit alcohol consumption.
- Lifestyle modifications: Nurses encourage patients to quit smoking, reduce stress, and adopt healthy lifestyle practices to promote overall well-being.
- Education and support: Nurses provide education about their condition, medication regimens, and lifestyle modifications. They also offer support and encouragement, fostering a sense of hope and empowerment.
Patient Education: Empowering the Individual
Providing clear and comprehensive education is crucial for patient empowerment. Nurses will:
- Explain the nature of the disease: Nurses thoroughly explain PUD, its causes, symptoms, and potential complications.
- Teach about medication regimens: Nurses emphasize the importance of medication adherence, explaining the purpose, dosage, side effects, and potential interactions of prescribed medications.
- Offer dietary guidance: Nurses provide advice on appropriate dietary choices, highlighting foods that may aggravate the ulcer, foods that can aid healing, and strategies for managing symptoms.
- Stress management techniques: Nurses emphasize the importance of managing stress and advise patients on techniques such as relaxation exercises, deep breathing, and mindfulness.
- Encourage healthy habits: Nurses reiterate the importance of quitting smoking, maintaining a healthy weight, and engaging in regular physical activity.
- Promote seeking early intervention: Nurses emphasize the importance of seeking medical attention promptly for any warning signs or worsening symptoms to prevent complications.
- Answer questions and address concerns: Nurses foster open communication, addressing any patient questions or anxieties regarding their condition and treatment.
Empowering Patients: Taking Charge of Your Health
Peptic ulcer disease can be a challenging condition, but having a strong understanding of the disease and the role of nursing care can empower you to manage your symptoms and support your healing.
Expert Tips and Strategies for Success
- Be an active participant in your care: Communicate openly with your healthcare providers, sharing your concerns and questions. Make sure you understand your diagnosis, treatment plan, and medication regimen.
- Follow your doctor’s instructions: Adhere to medication schedules, dietary recommendations, and lifestyle changes advised by your healthcare providers.
- Keep a symptom diary: This can help track pain frequency, severity, and contributing factors, enabling you to better communicate with your healthcare team.
- Learn stress management techniques: Explore techniques like deep breathing, relaxation exercises, meditation, or yoga to minimize stress levels.
- Join a support group: Connecting with others who have peptic ulcer disease can provide a sense of community and valuable insights.
Nursing Diagnosis For Peptic Ulcer Disease
Conclusion: Navigating the Path to Recovery
Peptic ulcer disease is a common condition, but with the right care, you can navigate the challenges and promote healing. Nurses play a critical role in providing compassionate care, education, and support, guiding patients on their journey to recovery. Remember, understanding your condition and actively participating in your care are key steps towards living a healthier, happier life despite the challenges of peptic ulcer disease. Stay informed, connect with your healthcare providers, and embrace the journey to healing.






